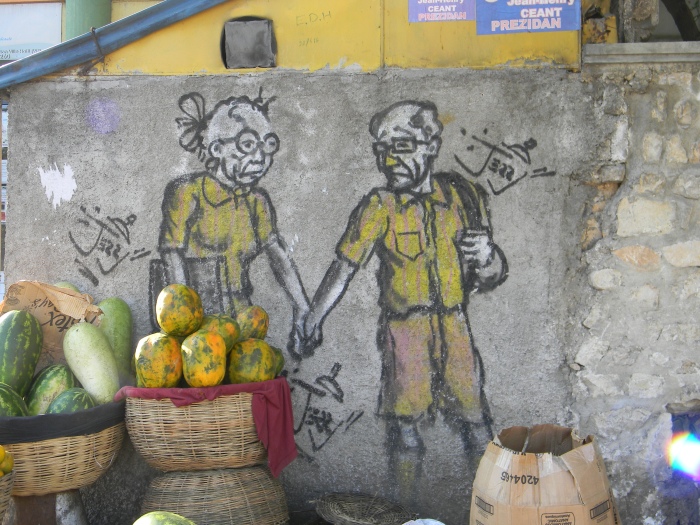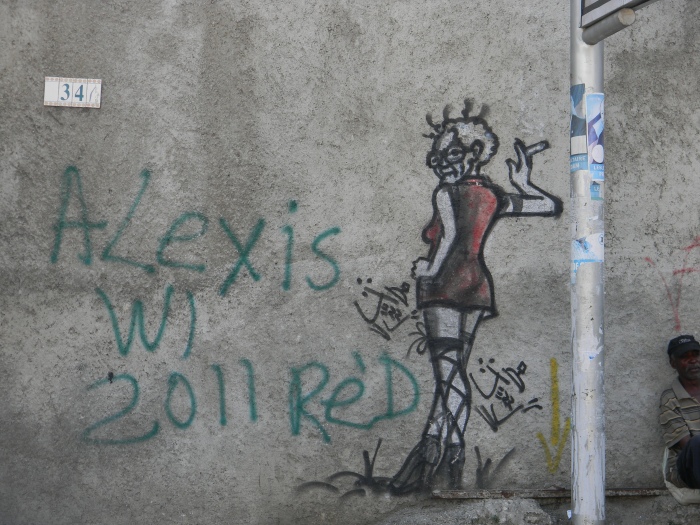There’s a long-standing tradition of political graffiti in Haiti—one that began soon after the Duvalier dictatorship ended its 29 year reign of terror with the ouster in 1986 of now newly-returned Baby Doc.
We’ve come full circle.
Duvalier is back. Aristide is on his way.
However, political graffiti isn’t gone. In fact, it’s virtually everywhere in Haiti’s capital—buildings and walls defaced by political thugs given $35 (US) and some spray paint to propagandize Port-au-Prince—scrawlings in red, black, and blue—the names of presidential candidates literally littering the city in ink.
What’s different, however, is this: there’s a new kid on the block, a graffiti artist named Jerry Rosembert Moise, who began his brilliant work just hours after an earthquake devastated his city.
What’s also different is that Jerry’s graffiti is decidedly non-political. It articulates the suffering of an otherwise silent city, whose pain is tented and tarped along rubble-strewn streets, where cholera rages and rioters react in a language of flaming tires—a solidarity of burning rubber.
Jerry, a twenty-five-year-old graphic artist by training, paints simultaneously with both hands. By now he’s completed more than 50 pieces, beginning in Port-au-Prince proper, before moving uptown to Petion-ville where we live.
Directly across the street from my partner Sara’s office, is a painting that looks like this:
Though getting good photos of this piece is now complicated by a billboad’s intrusion, you can still see the ball-holding boy, watching the world cup. There’s a lot of watching going on here, the person on the street seeing the painting, the young man staring at the set. Passively the world watches and plays games, while Haitians wait, forced to make furniture from rubble? Who holds the ball here? Are these the questions Jerry asks?
Just half way up the block, however, on the same side of the street is a piece that looks like this:
What’s Jerry’s message here? The hand-holding couple walk in solidarity. What makes them so sad, so tired? Why do they look down instead of up or at one another?
Still further up the block and across the street from Sara’s second office is a woman leaning against the very wall she’s painted on:
Her gaze is directed over her shoulder and into the street, perhaps even across the road at the NGO where Sara works. She wears glasses, smokes a cigarette in high heels that force her to stand on tip-toe, legs crossed—tentatively. She’s suggestively watching what? What does she need assistance seeing or saying? When does “suggestively” become “suggest?”
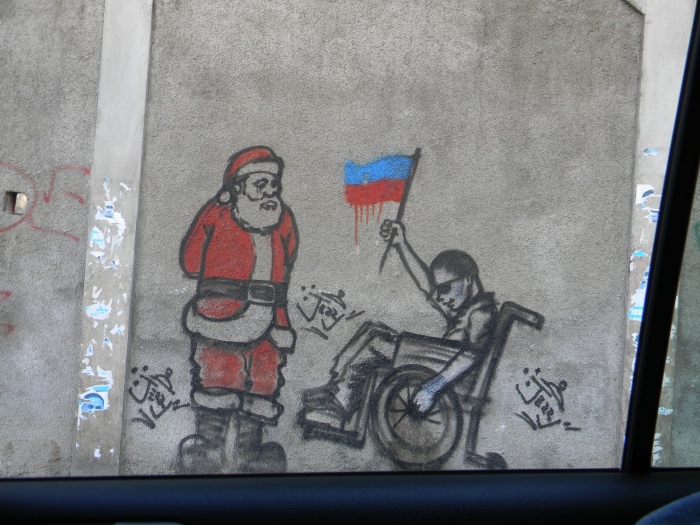
Not far from the block where these three pieces peer at televisions and NGOs, is an even sadder commentary of post-earthquake Haiti:
Here the boy in a wheel chair is watched by Santa Clause. Santa, suited up in high holiday-fashion, is the passive on-looker. The boy participates, waving a bleeding Haitian flag, popping a wheely—stunting for Santa.
“I may be hurt,” he says.
“I may be bleeding. But watch me wave patriotically, while you stand idly by, hot under the collar in that stupid European suit!”
“Why are all the ex-pats pissed?” he wants to know.
Santa may not know the answer. We may not either. But Jerry himself has this to say:
So Jerry’s message is one of hope, a belief that the youth of Haiti can and will make a difference, build a stronger future on the rubble that is now.
Tomorrow, an update on Jerry’s latest project!
Stay tuned.